Qwen3模型架构
这篇blog以Qwen3为例,介绍目前主流GPT架构中使用到的一些模块。
旋转位置编码(RoPE)
绝对位置编码具有实现简单、计算速度快等优点,而相对位置编码则更吻合我们的直觉,实际性能往往也更好。RoPE则集各家之长,实现了“以绝对位置编码的方式实现相对位置编码”。
RoPE希望的建模目标为:找到一个函数$f$,使得如下关系成立
\[f(q, m) \cdot f(k, n) = g(q, k, m - n)\]其中,$f$是把位置信息结合到query/key embeddings的机制。$g$是以query/key embedidings和相对位置$m - n$为输入的函数。该函数的左边是以绝对位置编码,而右边是实现了相对位置编码。
RoPE得到的最终函数$f$为
\[f(q, m) = R_mq = \begin{pmatrix} \cos m\theta & -\sin m\theta \\ \sin m\theta & \cos m\theta \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} p_0 \\ p_1 \end{pmatrix}\]左侧的$R_m$是一个旋转矩阵,$f(q, m)$表示在保持向量$q$的模长的同时,将其逆时针旋转$m\theta$。这意味着只需要装将向量旋转某个角度,即可实现对该向量添加绝对位置信息,这就是旋转位置编码的由来。
进一步验证RoPE以绝对位置编码实现相对位置编码
\[\begin{align} q_m \cdot k_n &= f(q, m) \cdot f(k, n) \\ &= (R_mq)^T * (R_nk) \\ &= q^TR_m^T * R_nk \\ &=q^T\begin{bmatrix} cos(n-m)\theta & -sin(n-m)\theta \\ sin(n-m)\theta & cos(n-m)\theta \end{bmatrix} k \\ &=q^TR_{n-m}k \end{align}\]为了把RoPE推广到高维向量,可以分而治之,把高维向量分为两两一组,分别旋转。这个公式表示为
\[\begin{pmatrix} \cos m\theta & -\sin m\theta & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ \sin m\theta & \cos m\theta & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \cos m\theta & -\sin m\theta & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \sin m\theta & \cos m\theta & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & \cos m\theta & -\sin m\theta\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & \sin m\theta & \cos m\theta\\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} q_0 \\ q_1 \\ q_2 \\ q_3 \\ \vdots \\ q_{d-2} \\ q_{d-1} \end{pmatrix}\]按照直觉,相对距离近的embedings应该有较强的attention,距离越远就越若,这也被称为远程衰减性。为了实现这个特性,RoPE借鉴了Sinusoidal位置编码,将每个分组的$\theta$设置为不同的常量,从而引入远程衰减的性质。设置$\theta_i = 10000^{-2i/d}$, 上个公式变为
\[\begin{pmatrix} \cos m\theta_0 & -\sin m\theta_0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ \sin m\theta_0 & \cos m\theta_0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \cos m\theta_1 & -\sin m\theta_1 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \sin m\theta_1 & \cos m\theta_1 & \ldots & 0 & 0 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & \cos m\theta_{d/2-1} & -\sin m\theta_{d/2-1}\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & \sin m\theta_{d/2-1} & \cos m\theta_{d/2-1}\\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} q_0 \\ q_1 \\ q_2 \\ q_3 \\ \vdots \\ q_{d-2} \\ q_{d-1} \end{pmatrix}\]上式中的旋转矩阵十分稀疏,为了节省算力,可以以下面的方式等效实现:
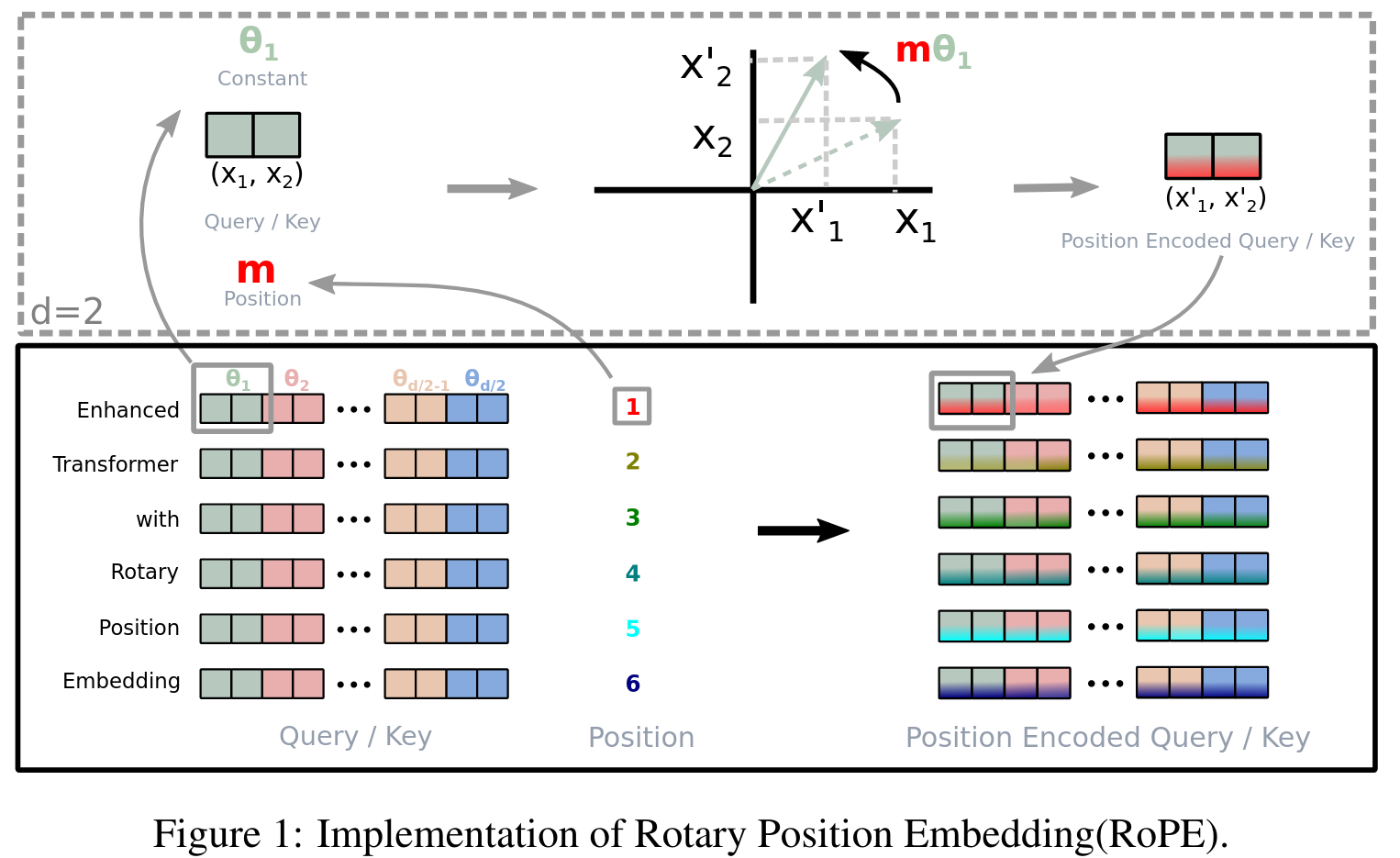
\[\begin{pmatrix} q_0 \\ q_1 \\ q_2 \\ q_3 \\ \cdot \\ q_{d-2} \\ q_{d-1} \\ \end{pmatrix} \otimes \begin{pmatrix} \cos m\theta_0 \\ \cos m\theta_0 \\ \cos m\theta_1 \\ \cos m\theta_1 \\ \cdot \\ \cos m\theta_{d/2-1} \\ \cos m\theta_{d/2-1} \\ \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} -q_1 \\ q_0 \\ -q_3 \\ q_2 \\ \cdot \\ -q_{d-1} \\ q_{d-2} \\ \end{pmatrix} \otimes \begin{pmatrix} \sin m\theta_0 \\ \sin m\theta_0 \\ \sin m\theta_1 \\ \sin m\theta_1 \\ \cdot \\ \sin m\theta_{d/2-1}\\ \sin m\theta_{d/2-1}\\ \end{pmatrix}\]RoPE的实现图解: